Best practices for enhancing security in fintech apps


The fintech industry has revolutionised how individuals and businesses interact with money-related services. From seamless transactions to instant loan approvals and AI-driven investments, fintech apps have become integral to modern financial systems. However, with great innovation comes significant risk. As digital financial services expand, so does the threat of cyber attackers exploiting security vulnerabilities in their systems.
This article explores the pressing need for robust fintech app security solutions, the key factors compromising security, and actionable strategies for building a proven security posture. By following these practices, organisations can safeguard their users, build trust, and ensure compliance with global regulations.
Table of contents
The Importance of Fintech Application Security
In the first half of 2024, a total capital of £2.4 billion was invested in European fintech companies. Sixty-five per cent of these funds were invested in UK brands, reinforcing this region’s leading position in the sector. In Q3, 2024, global funding for fintechs reached $7.3 billion. The constant growth within the sector, especially in less saturated markets, is driven by the increasing demand for seamless financial transactions, personalised banking experiences, and instant access to money-related services. However, the same technologies that enable these advancements can also compromise fintech app security. The more sensitive customer data is stored, processed, and transmitted through fintech apps, the greater the likelihood of hacker attacks and data breaches.
Compared to other industries, the financial services sector handles vast amounts of critical data, including bank account information, transaction history, credit card numbers, and even biometric identifiers. Unlike general user data, financial data is directly linked to monetary value, making it a prime target for exploitation.

According to Statista, in 2024, the average cost of a data breach across all studied industries was $4.88 million, while in the financial sector it was $6.08 million. Beyond financial loss, the reputational damage to organisations is often irreparable. That’s why fintech companies must invest heavily in protecting data, building secure identification solutions, and hiring app developers with expertise in creating secure systems.
Understanding the Cybersecurity Threat Landscape in Fintech
The financial services industry operates in a highly dynamic and vulnerable environment, where attackers constantly exploit potential vulnerabilities. Understanding common cyber threats is crucial to developing an effective security strategy that safeguards financial data. A multi-layered approach combining cutting-edge technologies, regulatory adherence, and proactive threat management is essential for mitigating risks and maintaining customer trust. Below is a list of challenges to be aware of:
Most Common Threats for Fintech Companies
Fintech apps face a variety of sophisticated cyber threats. Online transactions can be compromised by the following challenges:
- Data breaches: Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in fintech app security systems to gain unauthorised access to financial data and other sensitive information. Stolen data is often used for fraud or sold on the dark web.
- Phishing: Attackers impersonate trusted entities to trick users into revealing login credentials, financial details, or other critical data. Phishing remains a leading cause of data breaches in fintech companies.
- Malware and viruses: These harmful programs can steal, corrupt, or destroy sensitive information, often compromising entire systems.
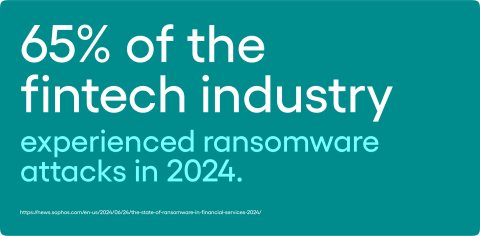
- Ransomware: A type of malware that encrypts a victim’s data and demands payment to unlock it. According to Sophos, 65% of the fintech industry experienced ransomware attacks in 2024.
- DDoS attacks: Distributed Denial of Service attacks flood fintech apps’ servers with excessive traffic, causing service disruptions. This can lead to downtime during crucial operational periods.
API Vulnerabilities
APIs are crucial to the financial industry, facilitating seamless integration with payment processors and third-party tools. However, inadequately secured APIs pose significant risks. Weak encryption or authentication mechanisms leave APIs vulnerable to interception and manipulation. Additionally, reliance on third-party providers introduces further risks, as a data breach in one provider can cascade across the network. A common issue is Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, where information is altered during the transmission of sensitive data. This often results from improper API configurations, emphasising the importance of prioritising security in fintech application development.
Fraud
Fraudulent activities continue to evolve, leveraging advanced technologies to exploit vulnerabilities in fintech systems. Mitigating financial fraud requires implementing sophisticated fraud detection systems, multi-factor authentication, and robust biometric verification. Common forms of fraud include:
- Identity theft: Using stolen credentials to impersonate legitimate users, often leading to fraudulent transactions and account takeovers.
- Fake or stolen identities: Fraudsters use fabricated or stolen identities to open accounts, apply for loans, or conduct illegal activities.
- Synthetic identity theft: Combining real and fake information to create entirely new identities used for fraudulent activities.
- Deepfakes and spoofing: Advanced technologies allow attackers to create fake biometric data, such as facial recognition patterns or voiceprints, to bypass security checks.
- Account takeovers: Using stolen credentials, attackers gain control over user accounts for financial gain.
Inadequate Encryption
Encryption is a cornerstone of data protection in the fintech industry. However, somemany fintech apps fail to implement it adequately, compromising their data security. Risks include unencrypted data transmission, where sensitive details like credit card numbers and login credentials can be intercepted. Additionally, outdated encryption standards are more easily cracked by attackers. Improper management of encryption keys further increases the risk of unauthorised access to systems, such as bank accounts or cloud servers.
To mitigate these vulnerabilities, fintech companies must adopt robust encryption protocols like AES-256 and TLS 1.3, ensuring that data in transit and at rest remains secure. Employing Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) for key storage and periodic key rotation further enhances protection. Engaging professional security testing teams to audit encryption and other vulnerabilities is also highly recommended.
Compliance and Regulatory Risks
Compliance with industry regulations is a critical aspect of fintech security, ensuring both the protection of consumer rights and the secure operation of financial systems. Non-compliance with key regulations such as PCI DSS, GDPR, CCPA, or PSD2 can lead to severe consequences, including hefty fines (e.g., €20 million or 4% of annual turnover for GDPR non-compliance), operational disruptions, and reputational damage. Regulatory investigations may halt services, while lawsuits from affected customers or authorities can compound financial and legal losses.

Key frameworks like PCI DSS enforce the secure handling of payment card data through encryption, monitoring, and strict access controls, while GDPR mandates that fintech companies protect EU consumer data and adhere to transparency standards. Similarly, CCPA grants California residents rights over their data, including deletion and opting out of sales, and PSD2 promotes Strong Customer Authentication (SCA) and secures open banking APIs in Europe.
Adherence to these regulations is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires consistent audits, updates to security policies, and the implementation of comprehensive compliance frameworks. Failure to comply not only impacts a company’s bottom line but also erodes trust, as consumers and investors are less likely to engage with organisations known for neglecting security practices.
Mobile App Security Threats

Since the volume of mobile payments is constantly increasing ($2.3 trillion in 2023 with a 16.6% annual increase), fintech companies must be aware that their mobile apps have become prime targets for attackers. Common vulnerabilities include weak authentication mechanisms, such as reliance on static passwords that are easily compromised, poorly written or outdated code that can be reverse-engineered to expose security flaws, and unencrypted data transmissions, which leave sensitive information vulnerable to interception. To address these risks, financial mobile apps must implement advanced security measures, including biometric and adaptive authentication, as well as code control, to enhance protection and maintain system integrity.
Insider Threats
Internal actors, whether through negligence or malicious intent, account for approximately 35% of data leakage situations in the financial sector. Insider threats can arise from employees mishandling sensitive personal data or failing to adhere to security protocols, as well as from deliberate actions, such as employees or contractors leaking or stealing data for personal gain. Mitigating these challenges requires implementing strict access controls, enforcing role-based access management, and conducting regular employee training.

Supply Chain Threats
The reliance on third-party software providers and cloud servers introduces vulnerabilities that are often beyond the direct control of fintech companies. Supply chain risks include breaches in vendor systems that can cascade to connected fintech apps, data leaks caused by poor security practices of third-party providers, and risks associated with cloud dependency. The latter, in particular, offers scalability but can also expose sensitive systems if not properly secured. Supply chain protection requires regular assessments of vendor security practices, strict contractual security requirements, and robust monitoring of third-party systems to ensure compliance and safety. Research shows, that third-parties were involved in 15% of data breaches in 2024.
Cross-Border Compliance Issues
Operating across multiple jurisdictions presents significant challenges for fintech companies, as they must navigate a patchwork of regulations that differ by region. These variations can pertain to data protection, consumer rights, or transaction security, often requiring businesses to adapt their processes to meet local legal requirements. Cross-border compliance involves addressing not only technical standards but also cultural and operational differences, such as data sovereignty laws that mandate where and how customer data can be stored or processed.
To manage these complexities, fintech companies must implement dynamic compliance frameworks that ensure consistency in security measures while adapting to regional legal requirements. This includes maintaining transparent data-handling practices, employing scalable systems capable of adhering to diverse regulations, and engaging with local legal experts to ensure all obligations are met. Failure to address these nuances can lead to operational disruptions, fines, and reputational harm, making robust cross-border compliance strategies essential for fintech operations in a global market.
Ten Tips for Enhancing Fintech App Security Solutions
Building a secure fintech application requires a multi-layered approach that integrates best practices at every stage of development and operations. Below are detailed steps to fortify security, tailored for financial institutions aiming to create financial apps with exceptional safety standards.
1. Adopting Secure Coding Practices
The foundation of any secure fintech app is high-quality coding. Developers must adhere to industry-recognised secure coding standards and continuously evaluate code for vulnerabilities. Using static and dynamic code analysis tools to detect issues such as buffer overflows and unsafe dependencies during fintech development is a proven approach that ensures the most sophisticated level of protection. Teams should also implement strict input validation to prevent attacks like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Regular updates of third-party libraries and frameworks allow programmers to patch known security flaws, ensuring external dependencies are as secure as internal code.
2. Implementing Code Obfuscation
Code obfuscation adds an essential layer of security by making app code difficult for attackers to interpret or reverse-engineer. Obfuscation techniques can conceal critical functions, algorithms, and encryption keys. Combining obfuscation with runtime application self-protection (RASP) tools enables active detection and blocking of unauthorised debugging attempts or code modifications.
3. Building a Secure Infrastructure
A resilient infrastructure forms the backbone of fintech security. This involves:
- Deploying Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) to isolate and secure sensitive data, preventing lateral movement by attackers.
- Implementing layered defences such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to identify and respond to cyber threats in real time.
- Embracing zero-trust architecture, which assumes no implicit trust and validates every access request through strict identity verification and contextual access policies.
4. Encrypting Data End-to-End
Encryption protects sensitive data during storage and transmission, making it unreadable to attackers. Key encryption practices include:
- Using advanced protocols like AES-256 for data at rest and TLS 1.3 for secure data transmissions.
- Employing hardware security modules (HSMs) for robust encryption key storage and management, reducing the risk of key exposure.
- Periodically rotating encryption keys to minimise exposure in case of compromise.
5. Strengthening Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication is an integral part of every secure fintech app. It protects user accounts from unwanted access. Several authentication methods can be incorporated into an application:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Combining something the user knows (passwords), something they have (tokens), and something they are (biometrics) for maximum security.
- Adaptive Authentication: Dynamically adjusting security requirements based on factors like login location, device data, or transaction size provides a balance between user experience and security.
- Biometric solutions: Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning offer reliable alternatives to traditional passwords, reducing the risk of stolen credentials.
6. Ensuring Third-Party Software and API Security
As mentioned earlier, APIs are crucial for fintech app security as they connect to other financial firms and third-party software providers. How can their security be managed? Implementing OAuth 2.0 or OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocols allows fintechs to manage secure access delegation and authentication. Regularly auditing third-party software integrations ensures that external components meet the brand’s specific security standards. Applying API rate-limiting and throttling mitigates Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks and reduces exposure to brute-force exploits.
7. Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are invaluable for detecting potential vulnerabilities and responding to emerging threats. Behavioural analytics can identify abnormal patterns, such as rapid multiple login attempts or unusual transaction volumes, that could indicate malicious activity. Real-time threat detection and response automation reduces the time needed to identify and neutralise an attack. Additionally, fraud detection models block suspicious activities, such as mismatched geolocations or inconsistent transaction behaviours.
8. Enforcing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures users have only the permissions necessary for their tasks, reducing the risk of unauthorised access. Defining clear roles with granular access privileges for administrators, regular users, auditors, and contractors is a state-of-the-art practice in the most secure fintech institutions. Just-in-time access policies are often used to provide temporary permissions for specific tasks, eliminating unnecessary long-term access. Regular auditing and reviewing of access logs are also integral parts of the RBAC routine, enabling responsible teams to identify potential misuse or privilege escalation attempts.
9. Conducting Regular Security Audits
Proactive security evaluations are vital for maintaining a strong security posture. Security teams should:
- Conduct penetration testing at least quarterly to simulate real-world attacks and uncover vulnerabilities.
- Use automated vulnerability scanners to identify and prioritise potential flaws across the application stack.
- Implement continuous monitoring solutions to detect and respond to anomalies in real time, ensuring ongoing protection.
10. Ensuring Regulatory Compliance Standards
Compliance is a cornerstone of fintech app security solutions. Beyond avoiding fines, it demonstrates a commitment to protecting customer data and meeting industry standards. That’s why fintech companies should establish compliance frameworks to address evolving regulations across regions, ensuring adherence to the laws mentioned above. Implementing tools to automate compliance checks, especially AI-powered ones, provides an opportunity to reduce human errors and speed up adaptation to regulatory changes. Moreover, money-related brands should maintain detailed documentation of security measures and audits to demonstrate compliance during inspections or legal reviews.
Conclusion
As fintech systems grow in sophistication, so do the methods employed by cyber attackers, making security a top priority at all times. Staying ahead requires a proactive and adaptive approach that leverages cutting-edge technologies, enforces strict compliance with evolving regulations, and implements comprehensive security strategies. By adopting the practices outlined in this article, fintech companies can not only protect their users and safeguard sensitive data but also prove their commitment to security, fostering trust and gaining a competitive advantage in the market.
The future of fintech security depends on innovation and preparation. Check out our article, How to Tackle Emerging Fintech Security Issues with Predictive Technologies. Learn how to use advanced technology to provide excellent safety measures for your customers, stakeholders, and employees, as well as future-proof your fintech products and services. We’ll gladly help with implementing these solutions.




