How is AI used in fintech? The transformation of customer service in finance

Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms proved itself to be particularly useful when it comes to customer service in various industries. AI in fintech already plays a significant role in fraud detection and data-driven decision-making. Since the financial sector has to handle a lot of inquiries, having automated assistance in answering them is highly appreciated. AI algorithms can categorize cases, attribute them to the right reps, and even answer complex questions regarding portfolio management, financial goals, or risk assessment. Depending on the used model and training data, they can reduce customer service workload even by 80%.
However, AI is not perfect and using it without caution to improve customer satisfaction can cause an opposite effect. Thus, this article focuses on the right approach to AI in fintech customer service. We will identify market trends, share best practices, point out the mistakes to avoid, and discuss how to approach AI introduction without disrupting current financial operations, but with leaving space for future improvements.
Table of contents
The Challenges of Customer Service in Fintech
Before we dive into the AI-driven solutions and how they can transform the finance industry, it’s crucial to understand the unique difficulties financial institutions have to face in order to deliver superior customer service. They showcase what exactly has to be taken care of and where are areas for improvement.

- High customer expectations: In an era of instant gratification, fintech users expect quick, accurate, and personalised responses to their queries and concerns.
- Complex offers: The fintech industry often provides comprehensive financial products and services that require in-depth data analysis.
- Financial technology expectations: Client satisfaction is directly correlated to the capabilities of the finance industry players to deliver more accurate credit scores, tailored financial advice, and precise fraud detection features.
- Regulatory compliance: The financial industry is heavily regulated, so financial service providers must navigate a complex web of rules and regulations.
- Data security concerns: With sensitive information at stake, ensuring financial data privacy and security during customer interactions is paramount.
- Scalability issues: As financial institutions grow, maintaining consistent service quality across an expanding customer base becomes increasingly challenging.
- Multichannel support: Customers expect seamless service across various platforms, including banking apps, websites, social media, and traditional phone support.
- 24/7 availability: The global nature of fintech demands round-the-clock access to often large customer service teams, which can require cost and time efficiency, as well as thought-through logistics.
- Language and cultural barriers: Many fintech companies operate internationally, requiring multilingual support and cultural sensitivity.
- Social role: The financial technology sector is expected to promote financial literacy with well-designed, user-friendly environments built based on historical data and market predictions.
These challenges have led many financial institutions to turn to AI algorithms. However, the enthusiasm for AI-driven customer service solutions has been tempered by the realities of implementation and return on investment. Let’s have a closer look at that.
The Use of AI in Business in 2024
Adoption market trends across numerous industries showcase a tendency that should not be ignored: AI and machine learning algorithms investments do not always provide expected enormous benefits. In their research report “Gen AI: Too Much Spend, Too Little Benefit”, Goldman Sachs raises this concern and tries to understand better why so many companies dived into the artificial intelligence boom without clear strategies or result KPIs, leading to overspending and growing costs in that area.
The document presents contrasting views on AI’s potential. Some analysts express scepticism about AI’s ability to solve complex problems and its high costs, while others are optimistic about its potential to automate work tasks, improve fraud detection, boost productivity, and drive business growth over the next decade. What are the main issues at the moment?
Many sectors were allured to AI by the promise of high productivity gains. However, these capabilities of AI algorithms are still limited, and it’s sometimes impossible to see spectacular results despite large investments. The unrealistic expectations and hype surrounding AI has led to inflated hopes that often don’t align with real-world outcomes.
Another alarming problem is a notable shortage of skilled professionals who can effectively implement and manage artificial intelligence systems. The same goes for data analytics experts. Many businesses struggle to integrate AI solutions with their existing architectures and processes, often having to pay more to update legacy apps so they can handle AI advancements. Without proper talent on board, it’s usually impossible to implement artificial intelligence models into corporate ecosystems without disruptions or malfunctions.
These findings suggest that the enthusiasm for solving customer service difficulties through AI is being tempered by the realities revealed in the report. Fintech companies, like businesses in other sectors, are discovering that implementing AI is not a remedy for every concern. It requires detailed planning, risk management, strategized execution, and post-deployment evaluation to deliver meaningful results. Fortunately, with the right support and aware approach, it’s possible to see true improvement with AI.
AI in Fintech for Customer Service Solutions
Despite what Goldman Sachs highlighted in their report, AI in fintech can revolutionize customer service. There are a few established directions to follow, with proven solutions that can be employed in the industry to showcase great results.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Chatbots and virtual assistants have been on the market for a long time. However, with the rapid development of AI solutions, they became more sophisticated and less unreal. AI-powered conversational interfaces can now interact with customers using natural language. In fintech, chatbots are often used to handle routine inquiries, provide account information, and guide users through basic financial transactions. Additionally, they can execute trades and perform advanced risk assessment. Automating financial processes and providing tailored financial advice is also something artificial intelligence technologies are used for.
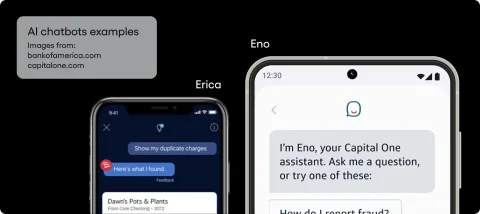
An example of a chatbot that succeeded in the financial sector is Erica, a virtual financial assistant provided by Bank of America to help customers with account-related queries and financial advice. Capital One’s Eno, a text-based chatbot that provides account insights and fraud detection alerts, is also considered a well-executed solution.
Statistics show that chatbots can handle up to 80% of queries for financial institutions. 65% of banks’ customers claim that 24/7 availability is the biggest benefit of using such solutions. Almost the same amount of consumers are ready to use virtual assistants instead of visiting a bank. 41% prefer this type of interaction for simple financial operations over using a mobile app or going to a physical branch. These numbers prove that AI-powered chatbots are already changing the financial landscape. However, it’s important to note that while chatbots and virtual assistants can handle many routine queries, they often struggle with complex issues or nuanced customer emotions, leading to potential frustration and the need for human intervention. The right balance between automated responses and real reps handling sensitive cases is a must.
Data Analytics and Automation
AI-powered data analysis is being used to collect and analyse vast amounts of customer and financial data, including transaction history, browsing behaviour, and customer service interactions. This information is crucial for understanding customer preferences and tailoring services accordingly. It’s worth mentioning that data is also used for fraud detection, credit scoring, and credit risk assessment.
However, the implementation of such systems is becoming increasingly complex due to evolving regulations, particularly the proposed AI Act in the European Union. This legislation aims to regulate the use of AI-powered systems, especially in high-risk areas like financial services.
Key considerations under the AI Act include:
- Restrictions on using personal data for profiling or influencing user behaviour.
- Requirements for transparency in AI data-driven decisions.
- Mandates for human oversight of artificial intelligence.
- Sophisticated risk management for the fintech industry.
AI Act and similar regulations will likely make it more challenging for fintech companies to leverage historical data for personalised customer experience, requiring them to implement innovation with an extra attention paid to regulatory compliance.
Personalised Customer Experience
AI in fintech enables companies to offer highly personalised customer experience in various ways. For instance, AI algorithms can analyse spending patterns and credit history to offer customised financial advice based on them. They also come useful in detailed credit scoring and more accurate risk assessments. Additionally, they can predict market trends and customer needs to proactively offer relevant products or services. For example, the AI-powered app Cleo uses natural language processing to provide individualised financial insights and advice through a conversational interface.
Artificial intelligence even made it possible to tailor user interfaces based on individual preferences and usage habits, helping customers to highly personalise the way they interact with financial software. It’s worth remembering that while personalisation can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, fintech companies must be cautious about crossing the line into invasive or manipulative practices, especially in light of upcoming AI regulations.
Benefits of Using AI in Fintech Customer Service
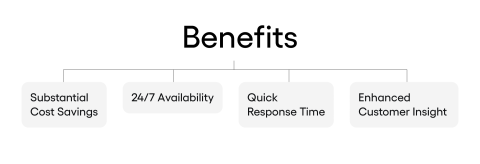
It seems that the challenges of AI in fintech adoption can’t be underestimated, but at the same time, the aware approach can bring multiple advantages to the financial industry. Let’s examine how this technology can effectively address potential drawbacks and what could be the potential effects:
Substantial Cost Savings
This is often cited as the most significant benefit of AI in fintech customer service, but it’s also the most challenging to achieve. Many financial institutions rush to implement AI solutions without thoroughly assessing their potential impact or conducting proper cost-benefit analyses.
Most companies don’t adequately evaluate the potential of AI applications before implementation. The ease of deployment frequently leads to hasty adoption, only to discover later that the AI solution may not be more effective than traditional methods.
It’s crucial to estimate the potential cost savings realistically and introduce the AI solution with proper caution, preferably step-by-step. This way, companies can evaluate if their goals are reached and adjust their strategies accordingly to avoid failures. Research shows that with such an approach when implementing chatbots and virtual assistants, banks can reduce customer support operational costs up to 30%. They can also significantly improve fraud detection and overall security budgets.
24/7 Availability
AI-powered systems can indeed provide round-the-clock customer support, addressing one of the key challenges in fintech customer service. This is particularly valuable for global companies serving customers across different time zones.
However, it’s crucial to ensure that the AI system can handle a wide range of queries effectively. Many financial institutions find that they still need human support available 24/7 to handle complex issues or escalations from the AI-powered systems.
By preparing the AI system beforehand with the right training data, financial institutions can make them more competent and responsive to a wide range of inquiries. It’s also important to provide a powerful infrastructure that will be able to handle hundreds of conversations at the same time. This way, human reps can only handle the most critical cases.
Quick Response Time
AI-powered chatbots can provide instant responses to customer queries, significantly reducing wait times. This addresses the high expectations of the fintech industry customers for quick service. Worldmetrics.org claims that “Chatbots can handle customer inquiries up to 10x faster than human agents in the banking industry.” This definitely proves that the usage of AI in fintech can lead to spectacular results when it comes to speeding up response times.
Enhanced Customer Insight
AI-powered financial data analysis can provide deep insights into customer credit history, behaviour, preferences, and needs. This can help fintech companies tailor their products and services more effectively, provide more accurate credit scores, and help their clients achieve their financial goals. Also, it’s crucial for successful early fraud detection. Nevertheless, as mentioned earlier, the use of such insights is becoming increasingly regulated, and companies must be careful about how they collect, analyse, and act upon customer data.
Challenges of AI in Fintech
Now we want to discuss the challenges of introducing AI in fintech. Even though it can offer several meaningful benefits, as we’ve mentioned earlier, it’s not always that simple. Numerous considerations must be addressed to ensure the success of AI-driven innovations in the fintech sector.
The Elusive Long-term Value of Machine Learning and AI Agents
As highlighted in the Goldman Sachs report, the real ROI from these investments is not always as expected. The main reasons include inadequate strategies and planning, lack of or poor integration with existing systems, insufficient training data, and usage of AI algorithms unable to handle complex or nuanced customer interactions.
To achieve true value of AI in fintech, they have to conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses before AI implementation. Also, it’s important to provide high-quality training data that can be continuously improved. Taking time to seamlessly integrate AI solutions with existing customer service processes is essential, especially when legacy systems are a part of the company’s ecosystem. Regular evaluation and adjustment of AI based on performance metrics is a good practice, too.
Data Privacy Requirements

Fintech companies handle sensitive financial information and private data of their customers, so security measures will always be on top of their priority lists. Especially, when introducing AI into their structures. Such innovative solutions must be designed with robust safety features in mind to protect customer data from breaches, unauthorised access, and all types of cyberthreats.
Moreover, companies must be transparent about how they collect, use, and store customer data, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR in Europe or the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the US.
The Impact of the AI Act on Regulatory Compliance
The mentioned-above AI Act in the European Union will have significant implications for the use of artificial intelligence in fintech customer service as well. Financial companies operating in or serving customers in the EU will need to carefully review their AI implementations to ensure compliance with these upcoming regulations.
The areas that will be influenced the most include:
- Risk classification: AI-powered systems in the fintech industry may be classified as high-risk, requiring constant, strict oversight and rigid compliance guidelines.
- Transparency demand: Companies will need to provide clear information about how AI make or influence decisions affecting customers.
- Human oversight: There will likely be mandates for human supervision of AI, particularly for high-stakes activities.
- Bias and fairness: AI will need to be regularly tested and monitored for potential biases or unfair outcomes.
Maintaining a Human Touch in Customer Service
While AI can handle many routine tasks efficiently, keeping a human element in customer service remains crucial, especially for complicated issues or emotional situations. Financial institutions need to strike a balance between AI efficiency and human empathy.
Strategies for maintaining the human touch include, first and foremost, clear escalation pathways from AI to customer service agents. AI algorithms should be trained to recognise emotional cues and transfer cases to human reps when appropriate. What’s most important though is to use AI to augment human work rather than replace them entirely. Personalising AI interactions to mimic human conversation patterns is possible to some extent, so it would be unwise to not keep customer support reps onboard.
The Future of Machine Learning and AI in Fintech Customer Service
Last but not least, it’s worth to discuss several emerging market trends that can shape the future of AI in fintech customer service.

The biggest impact will probably have the introduction of the AI Act and similar regulations worldwide. They will significantly shape how AI algorithms are used by financial institutions. Companies will need to invest in compliance measures and potentially redesign their AI systems to meet new standards. That’s why it’s so crucial to prepare flexible infrastructures for them. This way, they can be future-proof and ready for quick updates.
We’re likely to see more sophisticated hybrid models of work that combine AI efficiency with human expertise and nuanced approach. These models will aim to provide the best of both worlds – quick, data-driven responses for routine queries and nuanced, empathetic handling of complex issues. Companies will also invest in various tools to support their customer service teams with automation. Credit scoring, risk management, and other processes that require a detailed approach will get even more accurate.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) technology improves significantly, which means that over time, AI will become so much better at understanding people and respond to nuanced customer queries. This will potentially reduce the need for human intervention, leading to the optimization of costs and resources, as well as enabling financial institutions to focus on developing ethical AI systems that will be transparent, fair, and respectful of customer privacy. Fintech companies will have to prioritize that to achieve and maintain customer trust.
The significance of predictive customer service will also rise, as AI systems are forecasted to evolve into that direction. AI algorithms will be capable to proactively address customer issues before they occur, based on pattern analysis of customer data, including numerous factors like behaviours, search, individual preferences, and history of financial transactions.
AI is destined to seamlessly integrate with other financial technologies and tools to create ultimate ecosystems. In customer service for the financial industry, this could mean connection with augmented reality solutions for more interactive customer experience or using advanced, third-party systems to ensure the highest level of security. AI-powered apps will also execute trades and assess credit risk.
Conclusion
Simply put, fintech companies must approach AI implementation strategically, with a clear focus on measurable outcomes and long-term value. This way, they can not only increase operational efficiency and get insights for data-driven decision-making. They can also promote financial inclusion for the future generations.
Ultimately, the success of AI in fintech customer service will depend on how well companies can integrate these technologies with human expertise, maintain a personal touch in customer interactions, and navigate the complex regulatory environment.
To learn more about the broader impact of generative AI on the fintech industry, be sure to check out our article on the subject.