How to tackle emerging fintech security issues with predictive technologies


Responsibility and security are two main characteristics sought by consumers when picking money-related brands to trust. Fintech security concerns can be effective in scaring users away, but that doesn’t have to be the case. Financial institutions can meet and exceed customer expectations while growing their businesses without major disruptions.
In this article, we’ll discuss safety challenges that are predicted to dominate the fintech scene in the latter part of 2024 and beyond. Our goal is to also explore predictive technologies that can help brands address them.
Table of contents
Security in the Fintech Industry
The fintech industry is an important player in the digital transformation realm, outrunning traditional financial services in offering innovative solutions for individual clients and businesses. From mobile banking and peer-to-peer payments to robo-advisors and multi-currency exchanges, the growth of this sector is fuelled by increasing consumer demand for convenient, accessible, and personalised financial services.
Since fintech firms handle vast amounts of sensitive financial data and facilitate large sums of money in transactions, they have become prime targets for cyberattacks, fraudulent transactions, and insider threats.
A single security breach can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and erosion of customer trust. Moreover, the interconnected nature of the financial ecosystem means that security incidents at one fintech company can have far-reaching consequences for the entire sector. That’s why it’s essential to know potential cybersecurity threats and ensure security in fintech systems no matter what.
Emerging Threats in the Fintech Ecosystem
As we look ahead to the upcoming months, several known and new security risks should be kept in mind. Here are our picks:
Increase in Cyberattacks
The frequency and sophistication of cyberattacks targeting the financial sector continue to rise at an alarming rate. According to recent statistics, the fintech industry remains one of the most targeted sectors for cybersecurity concerns. In 2023, 22% of all attacks worldwide were directed at financial institutions, putting them in second place, just behind the technology sector.
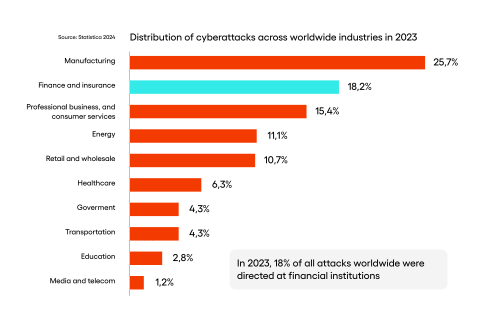
Cyber attackers exploit vulnerabilities with such methods as ransomware, phishing attacks, malware attacks, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and advanced persistent threats (APTs) becoming increasingly common. Fintech companies must introduce the best practices to defend against a wide range of attack vectors, from threat intelligence to intrusion detection systems and regular security audits.
Data Breaches
As fintech companies collect and process enormous volumes of personal and financial data, the risk of data breaches (that can lead to, for example, phishing attacks and identity theft) remains a significant concern. The Kroll Data Breach Outlook 2024 report highlights that the financial services sector continues to be one of the most affected industries when it comes to such security incidents.
The consequences of sensitive financial data breaches can be severe, including severe financial penalties and long-term damage to customer trust. Fintech companies must prioritise customers’ data protection measures, including strict access controls, robust encryption, safe data storage, and ongoing monitoring of data access points.
Unreliable Authentication Mechanisms
As traditional password-based authentication methods become increasingly vulnerable to attacks, fintech firms are under pressure to implement more secure and user-friendly authentication mechanisms. However, finding the right balance between security measures and user experience remains a challenge.
Multifactor authentication (MFA) has become a standard practice, but even this is not foolproof. Sophisticated attackers are finding ways to bypass MFA through techniques such as SIM swapping or man-in-the-middle attacks. Fintech companies need to explore more advanced authentication methods, such as biometrics and behavioural analytics, with thorough due diligence.
Regulatory Compliance
The financial industry is obliged to comply with regulatory compliance requirements. Guidelines can vary across different jurisdictions. As regulators struggle to keep pace with rapid technological advancements, fintech companies face the challenge of navigating a constantly evolving compliance workflows and best practices.
In 2024, we can expect to see increased efforts to identify vulnerabilities and protect sensitive data with key regulations, including General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), anti-money laundering (AML), and know-your-customer (KYC). Each of the fintech companies will need to invest in a robust compliance program to ensure they are always up-to-date with regulatory changes.
Third-party Vulnerabilities
Many fintech companies rely on a complex network of third-party vendors and partners to deliver their services. While this can drive innovation, efficiency, and resource savings, it also introduces potential security vulnerabilities. A security breach at a third-party provider can have negative outcomes for the fintech brand and its customers.
In 2024 and beyond, we can expect to see an increased focus on supply chain security protocols, increased access controls, and third-party risk management. Fintech companies will need to implement rigorous vendor assessment processes and continuous monitoring of third-party vendors risks.
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
APTs represent particularly insidious cyber threats to the fintech sector. These long-term, targeted attacks are often orchestrated by well-resourced cyber criminals, including nation-states and organised crime groups. APTs can remain undetected for extended periods, allowing attackers to gather sensitive financial information or manipulate financial systems.
Defending against APTs requires a multi-layered approach, including advanced security threats detection systems, regular security assessments, and robust incident response plans.
Money Laundering
As cryptocurrencies and other digital assets gain mainstream adoption, money laundering remains a significant concern for the fintech sector. According to Chainalysis, while the total volume of cryptocurrency-based money laundering decreased in 2023, the complexity and sophistication of laundering techniques have increased.
Fintech companies, particularly those operating in the cryptocurrency space, will need to implement advanced AML measures and work closely with regulators to combat potential threats.
Cybersecurity Risks Posed by Employees or Contractors
Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, continue to pose a significant risk to financial institutions. Employees and contractors with privileged access to systems and financial data can potentially cause substantial damage if robust security measures are not in place.
In the months to come, we can expect to see an increased focus on insider threat prevention, including strict access controls, employee monitoring systems, and regular cybersecurity training.
Predictive Technologies to Support Fintech Security
Since the fintech cybersecurity risks are quite broad and versatile, money-related businesses are turning to advanced predictive technologies to boost their protective measures. We’ve picked some of the emerging technologies that are currently on the rise in terms of addressing safety challenges for the fintech industry.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML)
AI and ML technologies can beare definitely game-changers when it comes to security protocols in the financial area. Algorithms can analyse vast amounts of sensitive data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate potential security threats. AI-powered systems can detect and respond to cyber threats faster and more accurately than traditional rule-based systems.
The main applications of artificial intelligence and ML models include fraud detection, anomalous activity detection, and risk assessment. By analysing transaction patterns and other operations, algorithms can learn normal system behaviours and flag any suspicious activities that may indicate a security breach or other type of threat. AI can also analyse various data points to predict potential security risks before they materialise.
Biometric Authentication
As we’ve mentioned above, traditional authentication methods are becoming increasingly unreliable. Thus, biometric authentication is emerging as a more secure alternative. Technologies such as fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and voice authentication enhance security while also being convenient and easy to use.
Advanced biometric systems are incorporating liveness detection and anti-spoofing measures to prevent sophisticated attacks. In 2024, we can expect to see wider adoption of multimodal biometric systems that combine multiple biometric factors for enhanced security.
Blockchain
While often associated with cryptocurrencies, blockchain technology has broader applications in fintech security. The decentralised nature of this technology makes it an attractive solution for various security-related use cases. For instance, blockchain-based digital identity solutions can provide a more secure and privacy-preserving alternative to traditional identity verification methods.
The immutable nature of blockchain can be leveraged to create secure, transparent audit trails for financial transactions, while smart contracts can automate and secure various financial processes, reducing the risk of financial fraud and human error. Blockchain is also considered foolproof technology for protected customer data storage.
Behavioural Analytics
Behavioural analytics technologies go beyond traditional security measures by analysing user behaviour patterns to detect potential threats. These systems can identify anomalies in user behaviour that may indicate account takeover attempts or insider threats.
Advanced behavioural analytics systems use machine learning algorithms to continuously learn and adapt to changing user behaviours, improving their accuracy over time. In 2024 and later on, we can expect to see increased integration of behavioural analytics into fintech security systems, providing an additional layer of protection against sophisticated attacks.
Quantum Computing
While still in its early stages of development, quantum computing is forecasted to take fintech security to the next level. On one hand, quantum computers are considered powerful enough to break many of the encryption algorithms currently used to secure financial transactions and data access. However, they also offer the potential for developing new, more secure encryption methods.
We can expect to see increased research and development in various areas of quantum computing in the next few years. Fintech companies are already preparing for the potential impact of this emerging trend on their security infrastructure.
Conclusion
The safety issues highlighted in this article require a proactive and multifaceted approach that can be achieved only with a high level of awareness and the right decisions when it comes to the implementation of protective measures.
Fintech companies need to adopt a holistic approach to safety, combining multiple technologies and best practices to create a complete, robust security ecosystem.
It’s also crucial to choose a software provider that is aware of security requirements and goals. Read our article on choosing the right partner for fintech development outsourcing to learn how to find a vendor that specialises in up-to-date technologies and regulatory frameworks.




